About the disease
A rapid severe life-threatening anaemia can also develop but this appears to be relatively rare from the cases we are aware of; in these cases it is possible that stressful situations may predispose to the development of clinical signs.
Pyruvate kinase deficiency is inherited and although predominantly a problem in the US it is being reported increasingly in cats throughout Australia, New Zealand and Europe, including the UK.
As described above, the clinical signs that develop can be serious and life threatening.
Carrier cats are clinically healthy and do not show clinical signs at all, but can pass the defective gene to their offspring.
The disease occurs when two Carrier cats are mated with each other. This is important because a large number of Carrier cats can arise in a population before PKDef is even noticed.
With any genetic disease, by the time the disease becomes an obvious problem within a population it is much more difficult to control and involves a lot more expense and heartbreak.
What breeds are affected - Abyssinian, Bengal, Egyptian Mau, La Perm, Maine Coon, Norwegian Forest, Savannah, Siberian, Singapura, Somali, Toyger, Tonkinese, Australian Mist, Asian, Aztec/Ocicat, Russian.
About the test
The Molecular Diagnostic Unit offers a genetic test to diagnose autosomal-recessive pyruvate kinase deficiency (PKDef) in cats. This genetic test is a PCR-based pyrosequencing assay that can reliably distinguish between Affected, Carrier and Normal cats.
It is highly recommended that all Abyssinian and Somali cats used for breeding are tested for the defective gene, as well as cats of these breeds showing signs of haemolytic anaemia. For Somali cats, testing for PKDef is now compulsory if cats are to be registered on the GCCF (Governing Council of the Cat Fancy) active register and used for breeding.
Please note: The test detects the Normal and Mutant PKDef genes found in domestic cats. The test also works in Bengal and Savannah cats, and detects the Asian Leopard Cat or Serval gene if present (i.e. in F1/F2 cats). There is no point in testing Asian Leopard Cats and Servals for PKDef since the mutant gene came from the domestic cat population.
Interpretation of results
A Normal autosomal recessive PKDef genetic test result means that the cat does not have the genetic mutation causing pyruvate kinase deficiency.
A Carrier autosomal recessive PKDef genetic test result means that the cat has one copy of the mutation. The cat will not have pyruvate kinase deficiency but may pass the mutation to their offspring.
An Affected autosomal recessive PKDef genetic test result means that the cat has two copies of the mutation. The cat will have pyruvate kinase deficiency.
Each certificate we issue will specify whether the cat is Normal, Carrier or Affected for the
autosomal recessive pyruvate kinase mutation.
What are the genetics of breeding?
My cat is Affected, should I neuter it?
Breeding is still possible
It is important to remember that genetic diseases are more likely to arise when the gene pool within a breed is small. This is typically the case in breeds with low numbers of cats that are related and often bred together. If a significant proportion of cats carry the defective gene for PKDef, neutering would only reduce the number available for breeding and, therefore, reduce the gene pool even further. This increases the chances of other genetic diseases arising.
There is no need to stop breeding, but it is important to ensure that you test for PKDef before breeding, and careful breeding programmes will be needed in order to gradually eliminate the disorder from the breed.
Should we breed from Affected cats?
Whilst it is preferable not to breed from Affected cats in the medium to longer term, in order to preserve the 'good genes' from Affected cats it is permissible to breed Affected cats with Normal cats (no copies of the defective gene). This does not risk producing any Affected kittens, but will produce Carrier cats. These Carrier cats can then be bred to other Normal cats, thereby producing more cats that are Normal and do not carry the defective gene. If this method is used to preserve breeding lines, it is preferable to use Affected male cats where possible as Affected females could become ill during pregnancy with risk of anaemia developing.
How do we breed safely?
Strategic and controlled breeding of Affected and Carrier cats to Normal cats is important for preserving the gene pool and retaining important lines.
It is preferable if the Affected cat is a male since a female could become ill during pregnancy.
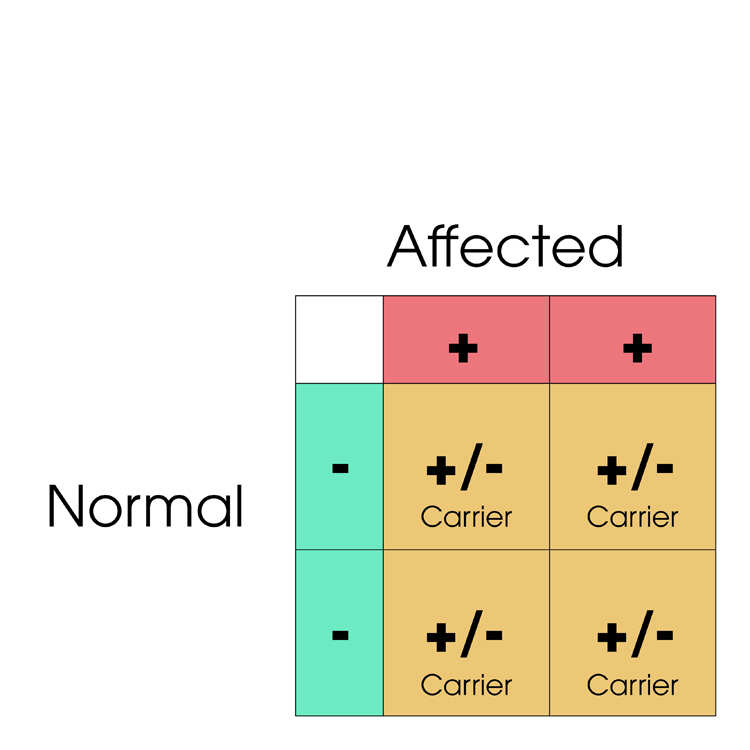
Cats have two copies of the PK gene, so can be Normal (-/-), Carrier (+/-) or Affected (+/+) depending on how many copies of the defective PK gene (+) they have. Below are shown various matings between Normal, Carrier and Affected cats.
Matings to avoid:

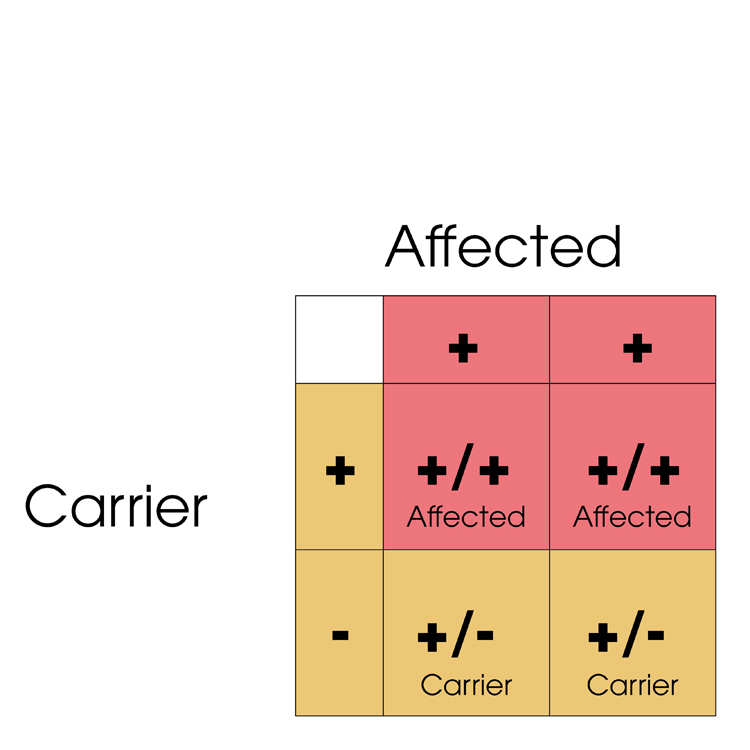
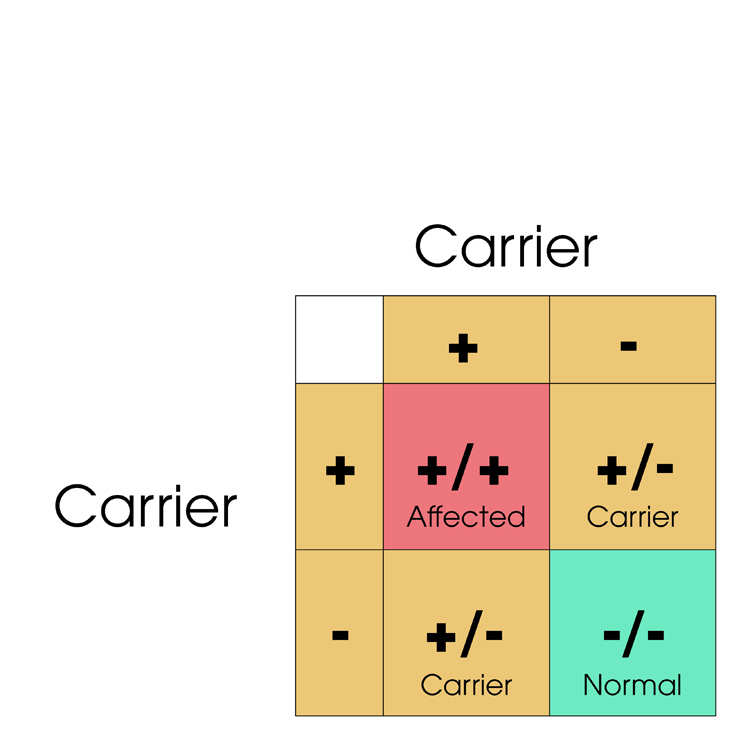
Matings that can be safely carried out:
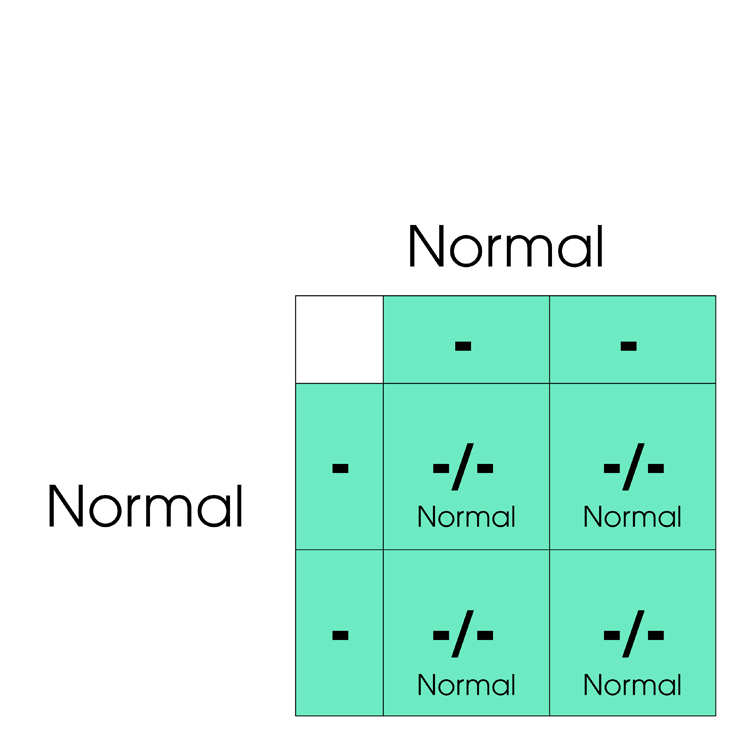
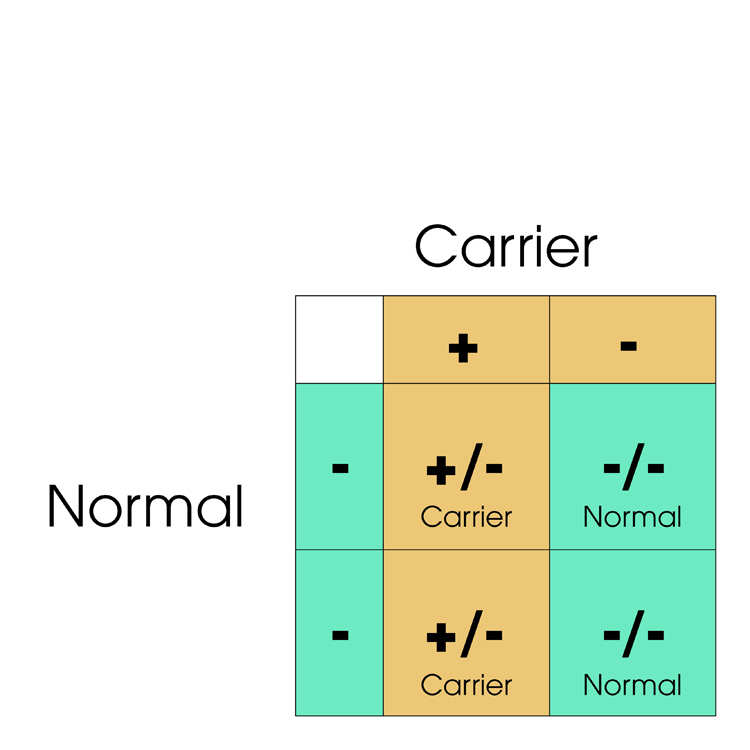
Frequently Asked Questions
Can my cat go on the ICC / GCCF negative registers?
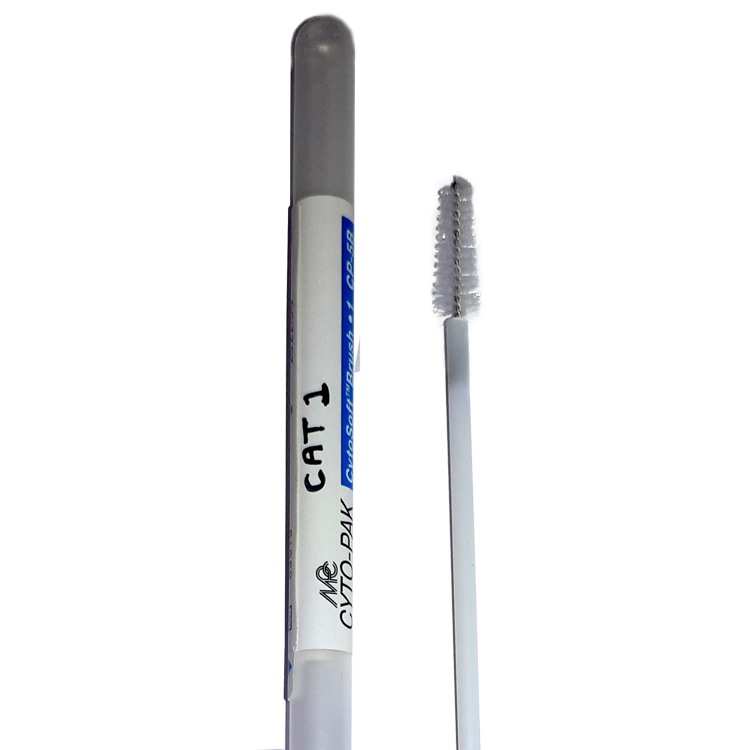
Yes it can! For cats to be placed on the negative register with organisations such as ICC or GCCF the sample (mouth swab or blood sample) MUST be taken by a vet who confirms the cat’s identity using its microchip number. The microchip number must be written on the submission form AND sample.
We have a dedicated submission form for this purpose, which both the owner and vet must complete. Our result certificate will state that the cat’s identity was confirmed by a vet and you can use this to register the cat on the ICC negative register.
If you DO NOT want your cat to go on these registers then you can take a mouth swab and submit it directly to the lab.
Click here to download -



